
Exploring the 3GPP AF – Application Function
Exploring the 3GPP AF – Application Function
Application Function (AF) in the 5G SBA
The Application Function (AF) is a powerful, yet often undervalued, Network Function (NF) in 4G and 5G networks. It plays a key role in traffic management and QoS assignments, through interaction with the policy elements. In a nutshell, it exposes the Application Layer for interaction with 5G NFs and network resources.
The AF resides in the control plane of the 5G Service-Based Architecture (SBA), and its main responsibilities include:
- Accessing the NEF for retrieving resources.
- Interacting with the Policy Control Function (PCF), enabling policy control.
- Traffic routing for applications
- Provides application services to subscribers.
Main responsibilities of the AF
The AF is defined in TS 29.517, which at the time of writing is at version 17.6.0. The 3GPP defines the AF as “a functional element that provides service- or application-related information to NF service consumers. The AF allows NF service consumers to subscribe to and unsubscribe from periodic notifications and/or notifications related to the detection of subscribed events.”
The AF also provides the Application Function Exposure Service, an important service that
allows NF service consumers to subscribe to, modify, and unsubscribe from application events, and notifies NF service consumers with a corresponding subscription about observed events on the AF.
The types of observed events include:
- AF application events exposed by the AF:
- Service Experience information for an application
- UE mobility information
- UE communication information
- Exceptions information
- User Data Congestion information
- Collective Behaviour information
- Dispersion information, and
- Performance Data information.
- UE application events exposed via Data Collection AF:
- QoE metrics
- Consumption reports
- Network Assistance invocations
- Charging and Policy invocations, and
- Media streaming access activity.
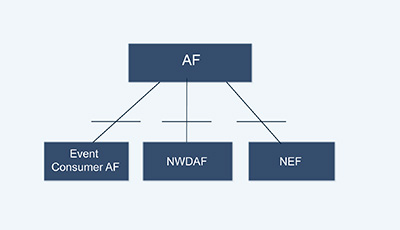
Furthermore, the Application Function Exposure Service (Naf_EventExposure) is part of the Naf service-based interface exhibited by the Application Function (AF), as shown in Figures 1a and 1b.
Figure 1a. Naf_EventExposure service Architecture, SBI representation
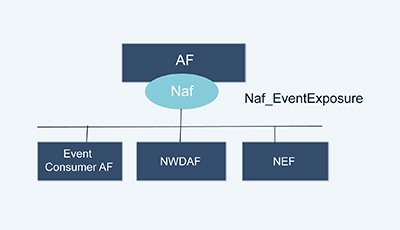
Figure 1b. Naf_EventExposure service Architecture, reference point representation
The Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF) is a 3GPP-defined solution that extracts and analyses data from the network to optimise its performance, reduce security risks and improve the subscribers’ quality of experience (QoE). As such, it’s a 3GPP standardised method of collecting data from user equipment, network functions, and operations, administration, and maintenance (OAM) systems, from 5G Core, Cloud, and Edge networks for analytics. It interacts closely with other elements, including the AF – helping to ensure that the required QoS is maintained.
Trusted and Untrusted Applications
Another essential point to highlight is that each application service – which can be Trusted or Untrusted – is likely to have its own AF, for example for video streaming, voice and video calls, messaging, social media, and so on.
Examples of Trusted (native) applications – which reside in a trusted data network and use the Network Repository Function (NEF) and so can interact directly 5GC NFs – include voice and video calls, SMS/messaging, V2X applications, XR applications.
Examples of Untrusted (OTT) applications – which reside externally in an untrusted data network and use the NEF for communication with the core – include mobile or internet browsing, WhatsApp/Skype/Messenger and so on, Netflix/YouTube and so on, and LinkedIn, Facebook and so on.
The AF also interacts with numerous interfaces. In the reference point architecture, it interacts with:
- N5 – the reference point between the Policy Control Function (PCF) and an AF.
- N33 – the reference point between Network Exposure Function (NEF) and AF.
- N57 – the reference point between AF and the UE radio Capability Management Function (UCMF).
In the SBA, Naf is the service-based interface offered by the AF.
The AF’s essential role in establishing QoS
In summary, the AF sits in the control plane and establishes QoS, and therefore QoE, for subscribers to a service or application and interacts with policy charging and rules functions. At the same time, every service or application – each with specific performance parameter requirements – may require its own AF. Of course, the 5G SBA is a complex and dynamic environment, requiring real-time orchestration of applications and services – including feedback from the NWDAF for real-time control and adjustment of QoS settings.
Playing such an important and central role, it’s therefore essential that network operators can test, validate and assure the performance of AFs, both in pre-production and live networks, across different networks (legacy and 5G), with different test cases scenarios, using different protocols simultaneously, and with full support for DevOps strategies.
How can Emblasoft help?
Emblasoft’s test and service assurance solutions have been developed around two core concepts: Simplicity and Flexibility. Emblasoft Evolver, for example, is simple to integrate and offers many preconfigured test scenarios to provide a baseline for future exploration.
REST API interfaces enable integration with orchestration platforms, providing full alignment with new deployment models. It enables hundreds of test cases and scenarios to be created and executed using distributed active agents to support CI/CD/CT models.
We also enable extensive active monitoring. As 5G services demand a broad range of different QoS settings, it’s essential to continuously validate service performance in live networks. Active monitoring is based on the deployment of software agents into live networks. They participate in real services and interact with delivery components, enabling the collection of real-time data to assess performance and the experience delivered to service users.
Emblasoft’s solutions are comprehensive and fully customisable with a powerful script editor enabling configuration of different user test case scenarios with extensive, flexible KPI reporting and alarms to provide instant feedback.
Our solutions enable end-to-end, automated test cases, including a library of preconfigured test scenarios, with full support for vendor-agnostic environments, to provide:
- Flexible Functional Testing of services and applications
Prove your services under extreme loads across multiple test case scenarios and validate new features with full support for CD/CI schedules.
- Innovative service development and delivery
Ensure the continuous, efficient development of delivery of new services and upgrades with powerful Performance Testing.
- Active monitoring
Continuous dynamic service assurance for near real-time service performance monitoring. Simulate from 1 to millions of users, and deploy hundreds of live software agents for continuous, active monitoring.
- Individual node testing and assurance
Test individual nodes and interfaces in isolation or in parallel to validate end-to-end functionality and performance.
- Automated testing in legacy and 5G networks
Fully automated, end-to-end, flexible testing, validation and service assurance for 2G-5G networks with support for multiple protocols simultaneously.
Importantly, Emblasoft’s solutions are fully automated and aligned with Operator DevOps release programmes and continuous innovation cycles. This ensures that service iterations can be tested effectively and automatically, supporting agile adoption of new services to support the dynamic changes that 5G offers.
Get in touch today to find out how Emblasoft’s powerful testing solutions can validate and optimise application and service performance in both pre-production and live environments, with full support for DevOps strategies.