
The ability to test N1 and N2 interface functionality at scale is key to 5G success
The ability to test N1 and N2 interface functionality at scale is key to 5G success
The N1 and N2 interfaces are crucial in mobility management within the 5G network, so comprehensive testing of N1/N2 interface functionality from the 5G NG-RAN / gNodeB is essential to ensure realistic load and subscriber behaviour simulation.
Mobility management is one of the core functions of any GSM, UMTS, LTE or 5G network. It allows the network to track where subscribers are, and to register, manage and authorise their connections to the network and the services they are subscribed to as they move between base stations.
Mobility management is key in any network
The Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) in 5G terminates the control plane of different access networks on to the 5G Core Network (5GCN), and controls which UEs (devices) can access the 5GCN and exchange traffic with Data Networks. As such, the AMF assumes control for mobility management and, where possible, manages roaming of UEs between gNBs in order to aid session continuity.
In LTE networks, the Mobility Management Entity (MME) controlled mobility management, but in the 5G era this cumbersome component has been separated into the AMF, the Session Management Function (SMF) and the Unified Data Management (UDM), as part of Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS), which was introduced in R14 to provide significantly greater flexibility and scalability in 5G networks.
The AMF coordinates network handovers between base stations, and allows users to connect to the 5G network and access the services they are subscribed to as they move around. As such, it helps manage the potentially massive number of devices (including IoT) that are connected to the 5G network, and is integral to mobility management.
The N1 and N2 interfaces are an essential component of the 5G AMF, and therefore vital in supporting CUPS, which decouples control signalling from user session traffic and therefore supports edge computing and a more distributed network architecture.
Figure 1 – 3GPP 5G Standalone service-based architecture
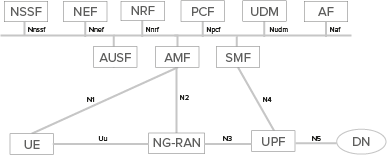
Source: Emblasoft
Why are the N1 and N2 interfaces so important?
The N1 interface is a transparent interface from the UE to the AMF, which transfers UE information (related to connection, mobility and sessions) to the AMF. In this respect, it’s similar to the NAS in 4G.
While N1 is transparent to the 5G RAN, N2 connects the gNodeB to the AMF and is therefore critical because, before a service can be accessed, the UE must be connected to the network.
Session control is now handled by the new Session Management Function (continuing the decomposition initiated with CUPS), while the UE context is the responsibility of the AMF. So, before any traffic or session can be initiated, the UE context, location and more need to be considered. That’s why N2 is so important – because it handles control-plane signalling.
Testing N1 and N2 interface functionality from the 5G NG-RAN / gNodeB is essential
Any 5G test solution must provide support for both N1 and N2 interfaces in order to generate and validate ‘real-world’ user traffic.
Testing 3GPP N1 and N2 interfaces is an essential task, as they enable the connection from the UE to the network and AMF. If you need to test service performance from the perspective of subscribers – connecting through the RAN to the core – then support for N1 and N2 is a necessity.
The AMF also coordinates network handovers between base stations – in other words, if you want to emulate subscriber mobility as part of behavioural testing, you need to be able to interact with the AMF via one of these interfaces.
Emblasoft offers full N1 and N2 interface support, allowing individual, customised testing – at scale (up to millions of subscribers) – for your 5G service assurance and node validation. It allows effective emulation of test messages from emulated UE devices to be sent to the AMF.
The Emblasoft testing solution offers different configurations, and can act as a gNodeB to enable validation – an essential step towards service verification. It also ensures performance under realistic load levels. Because each can be configured with different criteria, fine-grained modelling can be achieved – ensuring that realistic traffic representing real subscribers in your network is used to emulate actual conditions.
Our solution provides full support for the N1/N2 interfaces, as specified in 3GPP TS 23.501. Our N1 support can simulate part of the UE, according to 3GPP TS 24.501 version 15.2.1 towards the AMF. Emblasoft N2 support, meanwhile, enables simulation of part of the NG-RAN, according to 3GPP TS 38.413 version 15.2.0, towards the AMF.
The Emblasoft solution provides support for a number of critical interface procedures, as well as N1 and N2 messages. As a result, not only can you validate N1 and N2 under lab conditions in test networks, you can also to test live networks, ensuring that they perform under different loads, with different traffic scenarios and for a realistically diverse mix of subscribers.
Consequently, the end-to-end characteristics of the whole 5G core network can be tested. Importantly, the Emblasoft solution also enables node-specific testing for different nodes in isolation – such as the AMF, SMF and others – AUSF, PCF, UDM, and so on.
This allows operators to test the network before and during deployment, as well as continuously, as part of DevOps delivery in live networks, and vendors to validate functionality for their commercial offers. This latter point is important, because securing multi-vendor networks is a key goal for many operators.
Furthermore, as network slicing becomes a commercial reality, our solution will also enable the validation of end-to-end performance and characteristics of different network slices, through emulation of the N1 and N2 interfaces. It means that our solution can help operators and vendors, offering a clear evolution path towards full-fledged 5G performance – and driving ROI through commercial services. To find out more, get in touch.